Laser-Based Alignment System Posted in: AR700 Laser Displacement Sensor – Tags: Academia University and Government Research
Last Updated: March 20, 2023
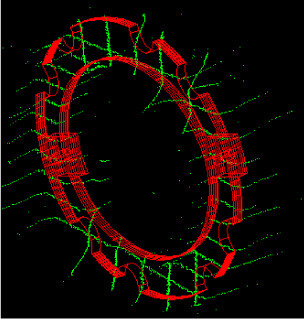
The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory at Michigan State University used a laser sensor in a system to measure the alignment of detectors. A full presentation of the project can be accessed from their website.
 Although now discontinued and replaced by the AR700 laser displacement sensor, Michigan State selected the AR600-6 with a 150 mm measurement range. The laser has a 5mW visible laser spot and has excellent sensitivity for measuring to shiny targets. The sensor was mounted to dual rotational stages to allow two degrees of freedom. Their system swept the laser spot across the target surface to create polar coordinates for a 3D profile.
Although now discontinued and replaced by the AR700 laser displacement sensor, Michigan State selected the AR600-6 with a 150 mm measurement range. The laser has a 5mW visible laser spot and has excellent sensitivity for measuring to shiny targets. The sensor was mounted to dual rotational stages to allow two degrees of freedom. Their system swept the laser spot across the target surface to create polar coordinates for a 3D profile.
Graduate students developed software to control the laser, scan edges with specified step sizes. Output is distance, theta’, and phi’; convert laser coordinates to spherical coordinates; correct position for off axis rotation; and combine different reference systems; convert positions to final lab reference frame of choice. For each 0.01° step in angle, the position resolution was ~0.2mm.
Related Products
Sarah has been our technical support and sales engineer for 5+ years. If you've ever reached out to Acuity Laser for tech support, more than likely, Sarah is the one who helped you.